Uncategorized
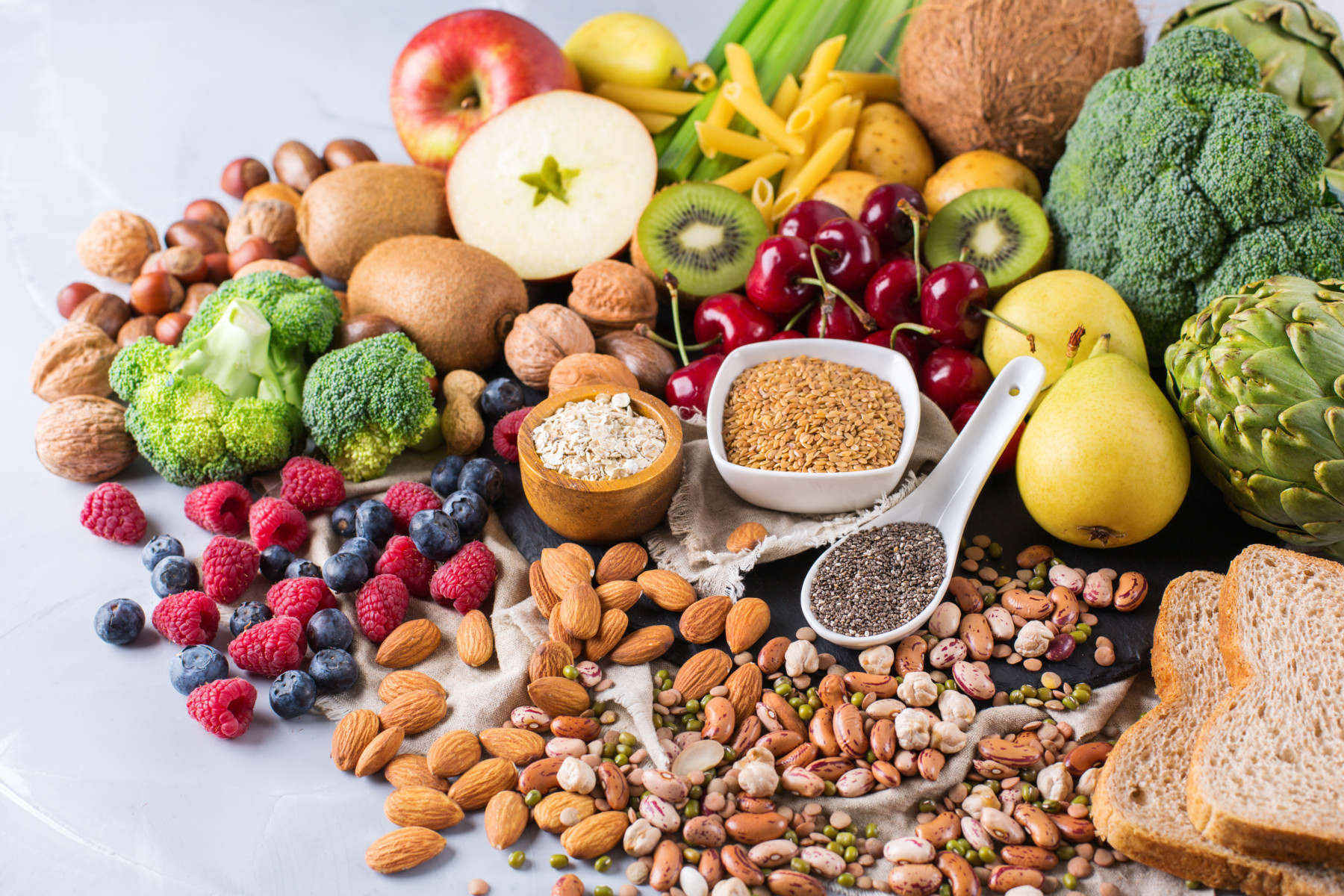
Strengthening Your Defense: How Antioxidants Enhance Immune Function and Protect Against Disease
Antioxidants are essential for maintaining good health and protecting our bodies from diseases. This blog post explains how these potent